Python Math Module
The math module is one of the most popular and commonly used modules in Python. As the name suggests, the math module contains pre-built mathematical operations.
Using it, we can import several useful functions that can help in performing mathematical operations. Moreover, the math module also contains mathematical constants.
The following are some of the uses of Python math module functions. (full list)
- Calculating factorials.
- Rounding off a float number.
- Solving quadric and trigonometric equations like sin, cos, tan, asin etc.
- Calculating the base to the exponent power.
- Calculating the square root of a number.
- calculating log
- calculating permutation and combination
Constants in Math Module
The math module also comes with some constants namely:
| Constant name | math module function | Symbol | Value | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pie | math.pi | π | 3.141592… | mathematical constant defined as ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter, |
| e | math.e | e | 2.718281 | Euler’s number |
| tau | math.tau | τ | 6.283185… | circle constant equal to 2π |
| infinity | math.inf | floating-point positive infinity equivalent to float(‘inf’) | ||
| not a number | math.nan | nan | equivalen to float(‘nan’) |
Import math
To use the functions and constants of math module we first import the built-in math module:
import mathInstead of importing the full module we can import cherry picked function by:
from math import <function-name>Functions in Math Module
Functions in math module are categorized based on there mathematical usage.
- Number-theoretic and representation functions
- Power and logarithmic functions
- Trigonometric functions
- Angular conversion
- Hyperbolic Functions
- Special functions
Example of some commonly used math module fuctions
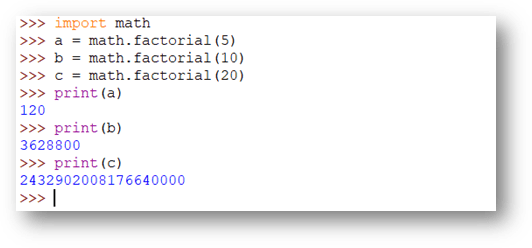
math.factorial()
The math.factorial() function is used to get the factorial of a number. Only positive integers are accepted by this function.
import math
a = math.factorial(5)
b = math.factorial(10)
c = math.factorial(20)
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
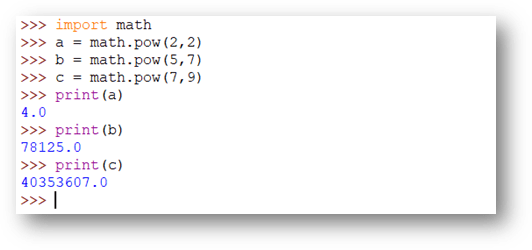
math.pow
The math.pow() function is to find the value of x raised to power y. It always returns a float value
import math
a = math.pow(2,2)
b = math.pow(5,7)
c = math.pow(7,9)
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
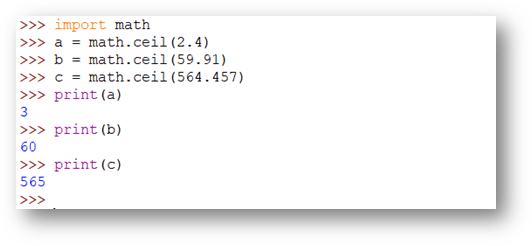
math.ceil and math.floor
The math.ceil() function returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to the number.
math.floor() function returns the largest integer less than or equal to the number.
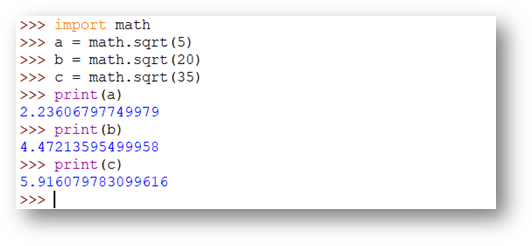
math.sqrt
The math.sqrt() function is used to find the square root of a number.
import math
a = math.sqrt(5)
b = math.sqrt(20)
c = math.sqrt(35)
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
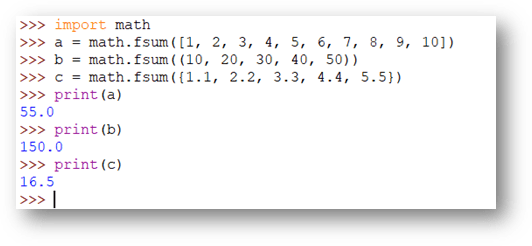
math.fsum
The math.fsum() function is used to find the sum of all the items of an iterable such as list, tuple, and set. It always returns a float value.
import math
a = math.fsum([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
b = math.fsum((10, 20, 30, 40, 50))
c = math.fsum({1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5})
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
Note: The functions in the math module do not accept complex values. To use complex values use cmath module instead.
List of All Math module Functions
Number-theoretic and representation functions
| Function Name | Usage |
|---|---|
| math.ceil(x) | returns smallest integer greater than or equal to x |
math.comb(n, k) | returns combination is a selection of items k from a collection n, such that the order of selection does not matter |
math.copysign(x, y) | returns x with sign of y |
math.fabs(x) | returns absolute value of x |
math.factorial(x) | returns factorial of an integer |
math.floor(x) | Return the floor of x, the largest integer less than or equal to x |
math.fmod(x, y) | Returns mod/ remainder of x/y. preferred when calculating mod of float numbers. Not equal to x%y operation |
| Return the mantissa and exponent of x as the pair (m, e) |
math.fsum(iterable) | Return an accurate floating point sum of values in the iterable. |
math.gcd(*integers) | Return the greatest common divisor of the specified integer arguments |
math.isclose(a, b, *, rel_tol=1e-09, abs_tol=0.0) | Return True if the values a and b are close to each other and False otherwise, rel_tol is the relative tolerance,abs_tol is the minimum absolute tolerance (read_more) |
math.isfinite(x) | Return True if x is neither an infinity nor a NaN, and False otherwise. |
math.isinf(x) | Return True if x is a positive or negative infinity, and False otherwise. |
math.isnan(x) | Return True if x is a NaN (not a number), and False otherwise. |
math.isqrt(n) | Return the integer square root of the nonnegative integer n |
math.lcm(*integers) | Return the least common multiple of the specified integer arguments |
math.ldexp(x, i) | Return x * (2**i) |
math.modf(x) | Return the fractional and integer parts of x. Both results carry the sign of x and are floats. |
math.nextafter(x, y) | Return the next floating-point value after x towards y. |
math.perm(n, k=None) | Permutation operation.Return the number of ways to choose k items from n items without repetition and with order. |
math.prod(iterable, *, start=1) | Calculate the product of all the elements in the input iterable. |
math.remainder(x, y) | Return the IEEE 754-style remainder of x with respect to y. |
math.trunc(x) | Return the real value x truncated to an integral |
math.ulp(x) | Return the value of the least significant bit of the float x |
Math Module Power and logarithmic functions
| Function Name | Usage |
|---|---|
math.exp(x) | Returns e raised to the power x |
math.expm1(x) | Return e raised to the power x, minus 1 |
math.log(x[, base]) | Return the natural logarithm of x to base . Calculated as log(x)/log(base) |
math.log1p(x) | Return the natural logarithm of 1+x (base e) |
math.log2(x) | Return the base-2 logarithm of x. |
math.log10(x) | Return the base-10 logarithm of x. |
math.pow(x, y) | Return x raised to the power y |
math.sqrt(x) | Return the square root of x. |
Math Module Trigonometric Functions
| Function name | Usage |
|---|---|
math.acos(x) | Return the arc cosine of x, in radians |
math.asin(x) | Return the arc sine of x, in radians. |
math.atan(x) | Return the arc tangent of x, in radians. |
math.atan2(y, x) | Return atan(y / x), in radians. |
math.cos(x) | Return the cosine of x radians. |
math.dist(p, q) | Return the Euclidean distance between two points p and q |
math.hypot(*coordinates) | Return the Euclidean norm. |
math.sin(x) | Return the sine of x radians. |
math.tan(x) | Return the tangent of x radians. |
Math Module Angular Conversion
| Function name | Usage |
|---|---|
math.degrees(x) | Convert angle x from radians to degrees. |
math.radians(x) | Convert angle x from degrees to radians. |
Math Module Hyperbolic Functions
| Function Name | Usage |
|---|---|
math.acosh(x) | Return the inverse hyperbolic cosine of x. |
math.asinh(x) | Return the inverse hyperbolic sine of x. |
math.atanh(x) | Return the inverse hyperbolic tangent of x. |
math.cosh(x) | Return the hyperbolic cosine of x. |
math.sinh(x) | Return the hyperbolic sine of x. |
math.tanh(x) | Return the hyperbolic tangent of x. |
Math Module Special Functions
| Function Name | Usage |
|---|---|
math.erf(x) | Return the error function at x. |
math.erfc(x) | Return the complementary error function at x. |
math.gamma(x) | Return the Gamma function at x. |
math.lgamma(x) | Return the natural logarithm of the absolute value of the Gamma function at x. |